Submitted by Penny Peck on Wed, 31/05/2023 - 23:59
The results of a collaborative research study led by Professors Edmund Kunji and Vera Moiseenkova-Bell, involving scientists from the Universities of Cambridge, Pennsylvania, East Anglia and Brussels, have been published in Science Advances.
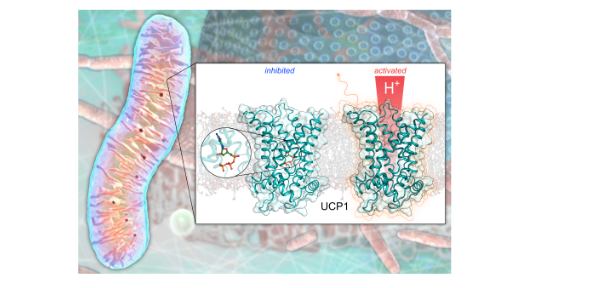
Uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) is the protein that allows specialised brown fat tissue, the “good fat”, to burn off calories as heat, in contrast to conventional white fat that stores calories on the body. Mammals switch on UCP1 activity in brown fat tissue to protect against the cold and to maintain body temperature, especially in new-borns, when shivering as a protective measure has not been developed. Increasing brown fat amounts in humans and activating UCP1 therapeutically is a potential way to combat obesity. Around two-thirds of UK adults are overweight or obese (NHS Health Survey for England, 2019). Obesity is linked to life-limiting conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and is a growing health problem. In addition to consuming fat, activated brown fat tissue can remove glucose from the blood, which can help control type 2 diabetes.
Despite more than 40 years of research on UCP1, the molecular mechanism of activation and inhibition were unresolved. The paper reveals, for the first time, the structure of UCP1 in atomic detail, and how its activity in brown fat cells can be inhibited by purine nucleotides, which are key regulatory molecules. These findings provide crucial molecular details that will help scientists develop therapeutics to activate UCP1 artificially in order to burn fat for the management of obesity and treatment of related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes. How UCP1 is activated has not been resolved, hampered by a lack of details on its molecular make up, so obtaining the first structural details is a significant breakthrough in this field.
Publication reference:
Jones, S. A., Gogoi, P., Ruprecht, J. J., King, M. S., Lee, Y., Zögg, T., Pardon, E., Chand, D., Steimle, S., Copeman, D. M., Cotrim, C. A., Steyaert, J., Crichton, P. G., Moiseenkova-Bell, V., & Kunji, E. R. S. (2023).
Structural basis of purine nucleotide inhibition of human uncoupling protein 1.
Science Advances 9, eadh4251. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIADV.ADH4251