PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY INVOLVING COMPLEX I
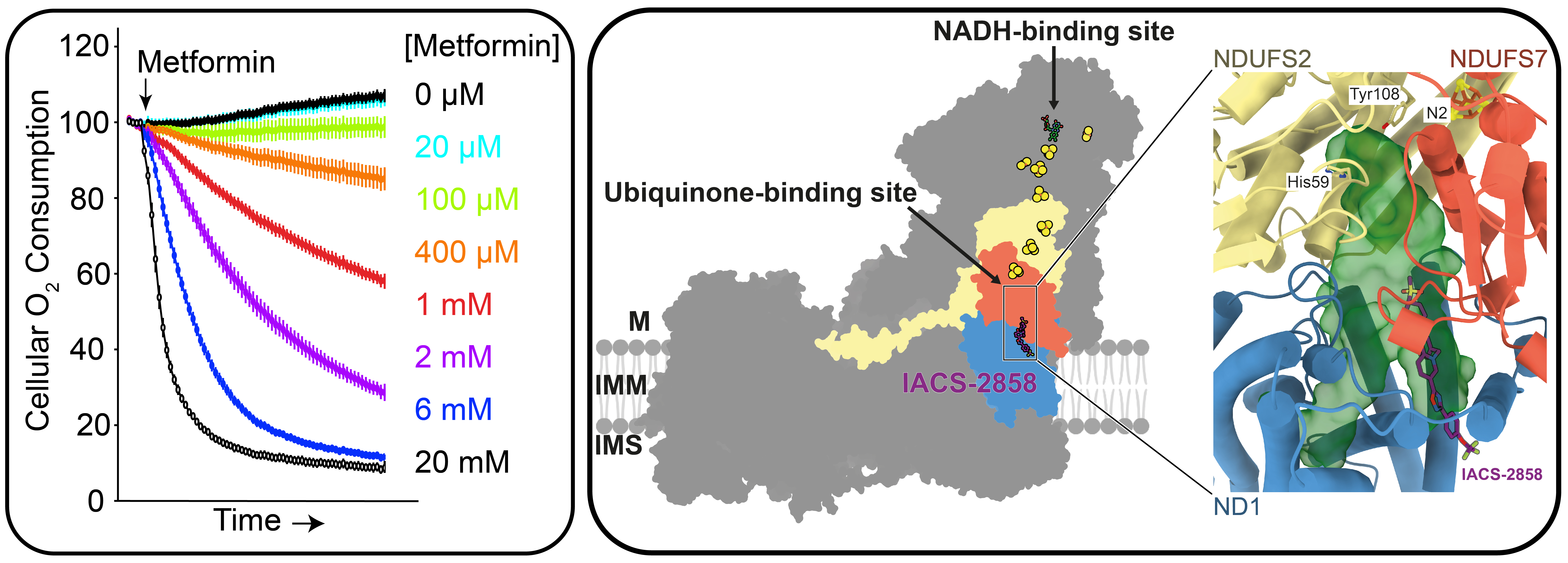
Figure Left: Inhibition of cellular oxygen consumption caused by inhibition of complex I by metformin [1], Right: Schematic and local structure of the binding site of IACS-2858 [2].
Due to the central role of complex I in cellular metabolism, it can be targeted by drugs to alter cellular processes such as redox balance, signalling pathways, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and ATP production. When complex I is the intended target these effects are clinically desirable, but at other times they represent damaging side reactions unrelated to the drug’s intended mechanism of action. A variety of compounds and drugs have been developed as intentional inhibitors of complex I catalysis, including IACS-010759 [2], [3], rotenoids [4] and biguanides [1], [5], which have all been proposed as anticancer agents. The role of complex I inhibition in the anti-diabetic effect of the widely-used drug metformin is still under debate. Other drugs inhibit complex I as an unwanted side-effect, impairing mitochondrial function [6]. Being able to determine when complex I is acting as an unwanted drug target is necessary for the development of safer drugs with fewer toxic side effects.
In our group we are beginning projects that:
- Survey complex I inhibition as a cause of liver toxicity by pharmacological compounds;
- Define the biochemical and structural bases of complex I-drug interactions;
- Pursue the cellular and mitochondrial consequences of complex I inhibition.
References
- Bridges HR, Jones JYJ, Pollak MN & Hirst J (2014)
Effects of metformin and other biguanides on oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria.
Biochem J 462, 475-487 - Chung I, Serreli R, Cross JB, Di Francesco ME, Marszalek JR & Hirst J (2021)
Cork-in-bottle mechanism of inhibitor binding to mammalian complex I.
Sci Adv 7, eabg4000 - Molina JR et al (2018)
An inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation exploits cancer vulnerability.
Nature Med 24, 1036-1046 - Russell DA, Bridges HR, Serreli R, Kidd SL, Mateu N, Osberger TJ, Sore HF, Hirst J & Spring DR (2020)
Hydroxylated rotenoids selectively inhibit the proliferation of prostate cancer cells.
J Nat Prod 83, 1829-1845 - Bridges HR, Sirviö VA, Agip A-NA & Hirst J (2016)
Molecular features of biguanides required for targeting of mitochondrial respiratory complex I and activation of AMP-kinase.
BMC Biol 14, 65 - Stephenson ZA, Harvey RF, Pryde KR, Mistry S, Hardy RE, Serreli R, Chung I, Allen TEH, Stoneley M, MacFarlane M, Fischer PM, Hirst J, Kellam B & Willis AE (2020)
Identification of a novel toxicophore in anti-cancer chemotherapeutics that targets mitochondrial respiratory complex I.
eLife 9, e55845